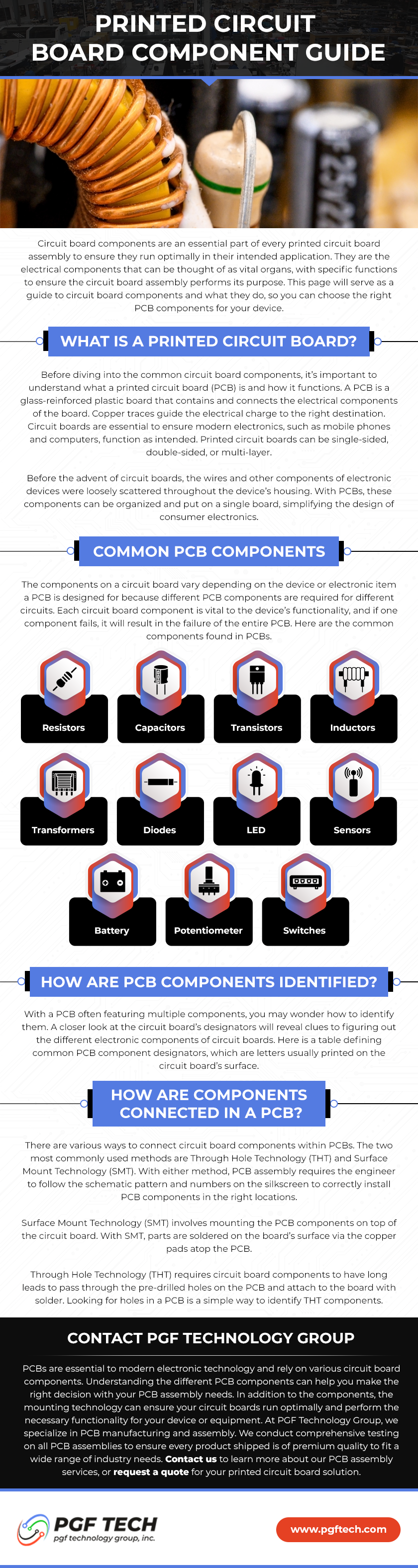
Charging Up
Electric Vehicles (EVs) are quickly charging up in the ranks as one of the most important innovations to watch in the coming years. Presently, the push to pump the breaks on CO2 emissions starts with determining the most significant contributing factor: gas-powered automobiles. Therefore, this “rEVolution” means assembling powerful components to ensure performance, longevity, and safety in an immediate timeframe. With this in mind, EV Power Cables drive forward with innovation to adhere to strict guidelines and certify proper conditions.
Here is a breakdown to amp up your knowledge about the top considerations for EV Power Cables during these changing times:
Critical Factors of the EV Power Cable
Seeing that the Electric Vehicle itself is on the cutting edge of technology, it would only make sense for the components involved to caravan behind. Hence, the regulations for EV Power Cables must reflect the industry’s future with added adaptability for the fast-changing times. By and large, these cable assemblies must be:
 Extremely Flexible
Extremely Flexible
Coupled with the Battery Management System (BMS) and various charging components, EV Power Cables must mold into different spaces to maintain balance in the vehicle and not obstruct any necessary operations.
UL-Listed
Underwriters’ Laboratories (UL) evaluates components for nationally recognized safety requirements for component manufacturing. At length, in a growing industry with many fresh ideas, increased testing shows responsibility for the drivers and manufacturers.
Compliant with RoHS
Similarly, if a product is certified by the Restriction of Certain Hazardous Substances (RoHS), its hard-to-dispose substances are limited to a set amount. Especially with the push for renewable energy sources, minimizing hazardous substances remains a top priority for each piece of the product.
Temperature-Controlled
When dealing with high-power electronics and batteries, heat becomes a central awareness topic. Cables must withstand heat to protect the inner layers and maintain the processes of the vehicle without becoming a hot mess.
Resistant to Chemicals, Cuts, Abrasion, and Crushing
Equally to heat resistance, the ability to withstand unwanted impacts or leaks marks a well-made EV Power Cable. When you enter your electric vehicle into the Monster Truck Rally, you need to know that the cables will last!
Supportive of Different Charging Modes
As stated above, adaptability for EV Cables must be the main factor for their assembly. With this in mind, EMS Providers must manufacture cable assemblies for every charging mode to power the vehicles correctly. Imagine how frustrating it is when your phone runs out of battery mid-call during an interview; now imagine your car in the middle of a snowstorm. Thus, assembling cables with these different charging modes is critical for safety and mental health:
- 1-phase AC charging for domestic connection
- 3-phase AC charging for domestic connection and public charging station
- DC charging for quick charging
Design Dilemma
Now that the requirements are established, another critical point becomes the design of this adaptable cable. Engineers must design cables to fit wherever needed while still providing the proper power. This design dilemma calls for:
Smaller Diameter
Reducing the size and weight of the power cable is always a requirement to downsize the drive train and trim vehicle weight. Besides reducing carbon emissions, the vehicle’s weight is another draw for prospective drivers who desire a change of pace.
Thick Outer-Layer
EV Power Cables must withstand road travel accidents, battery leakage, and user error. Indeed, the idea of having thick skin applies in a more literal sense to this electrical assembly.
Copper
Chiefly, copper electrical wires are safer to use than wires made of most other conductive metals because they are resistant to heat.
Copper is the preferred metal for electrical wires because of its high electrical conductivity, inexpensive, malleable, and thermally resistant properties. These details make it the universally accepted standard for manufacturing electrical wires.
Assembly Process
Tooling for Heavy Gauge Cables
We process our wiring for cables by using both automated and manual methods. This combination guarantees accurate work and checkpoints for assembly finalization.
At PGF, our Wire Processing Center and Cable Assembly Work Stations turn a grouping of wires and jackets into a functioning EV Power Cable. To learn more about our distinct processes, visit our PCBA and Cable Assemblies in EV Applications page.
Automated Assembly
Whenever possible, Schleuniger’s Manufacturing Machines assist in the automated operation of processes, mainly the following functions: Cutting, Stripping, and Terminating. For further uses, they are also handy (or should I say machine-y) for crimping and wire twisting.
Manual Assembly
In the next steps for projects, manual assembly is necessary for connector layout and visual inspection. Trained personnel can take a hands-on approach to finalizing and testing the assembly for the highest quality output.
Quality Testing
PGF goes through multiple rounds of testing to provide customers with durable, long-lasting cable assemblies. Our team utilizes:
- Pull-Testing Machines
- Schleuniger’s Inspection Machines
- UL Standard Inspection
- IPC 610 Class 2 and 3 Trained Personnel
Field Applications
EV Power Cables are essential for in-vehicle function and performance. Their applications range across many avenues, but ultimately, they connect and transfer power to crucial components of whichever vehicle they are implemented. Overall, they create a network of intelligence that allows the completed project to function correctly.
Power cables connect the inverter with two three-phase alternating currents (AC) motors, one for driving and generating electricity.
Many updated industries:
- Automotive
- Automatic Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
- High-Lows
- Helicopters
- Public Transportation
- School Buses
- Aerospace
- Battery Charging
Above all, noticing the constant updates to this industry as a whole, knowing that influential minds are innovating every component, is reassuring for electric manufacturing and should amp up solutions providers who have the opportunity to grow.

 Extremely Flexible
Extremely Flexible