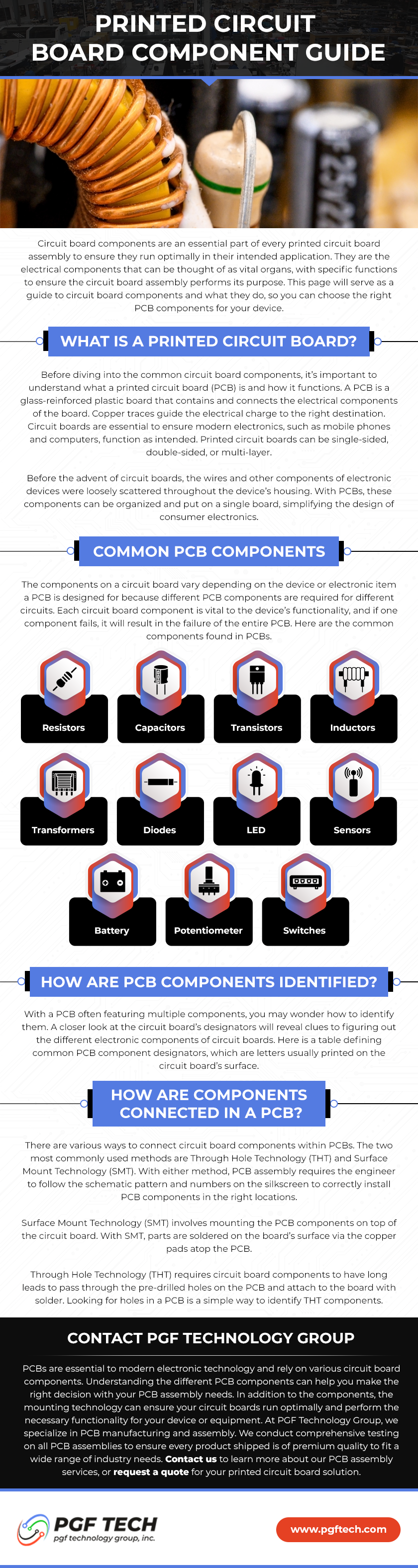
As the technological landscape continues to evolve, custom Printed Circuit Board Assemblies (PCBAs) have become integral components in the development of cutting-edge electronic devices. At PGF Technology Group, a leading custom manufacturer specializing in printed circuit boards, cables, wire harnesses, and box builds, we understand that navigating the complexities of custom PCBA projects can be overwhelming. In this comprehensive guide, we address frequently asked questions to provide clarity and insight into the world of custom electronic assemblies.
1. What is the significance of custom PCBA in electronic manufacturing?
Custom PCBA plays a pivotal role in electronic manufacturing by providing tailored solutions to meet specific design requirements. It allows for the integration of unique features, dimensions, and functionalities, offering a level of customization that off-the-shelf solutions cannot match.
- Tailored Designs: Custom PCBA allows manufacturers to design and develop electronic products with specific features and functionalities tailored to meet the unique requirements of a particular application or industry. This level of customization is crucial in industries where standard off-the-shelf solutions may not suffice.
- Optimized Performance: By customizing the PCBA, manufacturers can optimize the performance of electronic devices. This includes choosing components that match the exact specifications needed for the intended purpose, resulting in improved efficiency and functionality.
- Space and Cost Efficiency: Custom PCBA enables designers to create compact and space-efficient electronic assemblies. This is particularly important for devices where size constraints are critical. Additionally, by carefully selecting components, manufacturers can often achieve cost savings by avoiding unnecessary features and using cost-effective alternatives.
- Quality Control: Custom PCBA allows for greater control over the quality of components and manufacturing processes. Manufacturers can choose high-quality components from reliable suppliers and implement stringent quality control measures throughout the assembly process, ensuring the reliability and durability of the final product.
- Innovation and Differentiation: Customization fosters innovation, allowing manufacturers to differentiate their products in the market. By incorporating unique features and functionalities, companies can gain a competitive edge and appeal to specific customer needs.
- Flexibility in Prototyping: Custom PCBA is particularly beneficial during the prototyping phase of product development. Designers can quickly iterate and test different configurations, ensuring that the final product meets performance requirements before mass production begins.
- Supply Chain Control: Custom PCBA provides greater control over the supply chain. Manufacturers can select suppliers based on factors such as quality, reliability, and cost, ensuring a stable supply of components for production.
- Adaptability to Industry Standards: In certain industries, adherence to specific standards is crucial. Custom PCBA allows manufacturers to design products that comply with industry standards and regulations, ensuring that the final products meet required certifications.
2. How does PGF Technology Group approach custom PCBA design?
At PGF, our approach to custom PCBA design begins with a collaborative process. Our skilled engineers work closely with clients to understand their project requirements, ensuring that the final design aligns with the intended functionality and form factor. This collaborative approach sets the stage for successful and customized electronic solutions.
- Design and Prototyping:
- Begin with a detailed design of the PCB layout and circuit schematic based on the specific requirements of the electronic device.
- Develop a prototype to validate the design and identify any potential issues.
- Component Selection:
- Choose components based on the design specifications, taking into consideration factors such as performance, reliability, and availability.
- Source components from reputable suppliers and verify their compatibility with the design.
- PCB Fabrication:
- Once the design is finalized, manufacture the PCB using the chosen materials and technologies.
- Ensure that the PCB layout adheres to industry standards and follows design best practices.
- Solder Paste Application:
- Apply solder paste to the PCB using a stencil. This paste will later facilitate the attachment of surface-mount components during the reflow soldering process.
- Component Placement:
- Use pick-and-place machines or manual assembly to accurately place surface-mount and through-hole components on the PCB.
- Verify component alignment and orientation according to the design specifications.
- Reflow Soldering:
- Subject the PCB to a reflow soldering process, where the solder paste is melted, forming solder joints that connect the components to the PCB.
- Ensure proper temperature profiles and dwell times to achieve reliable solder joints.
- Inspection and Quality Control:
- Inspect the assembled PCB for defects, such as solder bridges, misalignments, or component damage.
- Use automated optical inspection (AOI) and other testing methods to verify the quality of solder joints and component placement.
- Functional Testing:
- Conduct functional testing to ensure that the assembled PCBA meets the specified performance criteria.
- Verify the functionality of individual components and the overall system.
- Programming and Firmware Installation:
- If applicable, program microcontrollers or install firmware on programmable devices.
- Ensure that the software is compatible with the hardware and functions as intended.
- Final Assembly:
- Complete any remaining assembly steps, such as attaching connectors, cables, or enclosures.
- Perform a final inspection to guarantee the overall integrity of the assembled device.
- Packaging and Shipping:
- Package the custom PCBA securely for protection during transportation.
- Ship the assembled PCBAs to the designated destination or integrate them into the final product assembly.
3. What industries benefit from custom PCBA solutions?
Custom PCBA solutions are versatile and cater to a wide range of industries. PGF’s expertise extends to automotive, healthcare, telecommunications, industrial automation, and more. Our adaptability allows us to meet the unique needs of diverse sectors.
4. How does PGF ensure the quality of its custom PCBA assemblies?
Quality is a top priority at PGF. Our custom PCBA assemblies undergo rigorous testing processes, including automated optical inspection (AOI) and functional testing, to ensure the highest standards of reliability and performance. We adhere to industry best practices to guarantee the quality of every assembly leaving our facility.
5. Can PGF handle both small-scale and large-scale custom PCBA production?
Yes, PGF is equipped to handle both small-scale and large-scale production runs. We are ideally set up for low volume, high mix projects, but we are flexible to each customer. Our scalable manufacturing processes allow us to accommodate a wide range of project sizes while maintaining efficiency and precision.
6. What types of materials does PGF use in custom PCBA manufacturing?
PGF Technology Group prioritizes the use of high-quality materials in custom PCBA manufacturing. We select substrates, resistors, capacitors, and other components carefully to ensure durability, reliability, and optimal electrical performance.
- Printed Circuit Board (PCB):
- Substrate Material: Common substrates include fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminates (FR-4), which is widely used for its durability and electrical properties.
- Copper Foil: A thin layer of copper is laminated onto the substrate. Copper provides the conductive pathways for electrical signals.
- Solder Paste:
- Flux: Solder paste contains flux, which helps remove oxidation from metal surfaces and promotes the wetting of solder to create reliable solder joints during the assembly process.
- Solder Mask:
- Epoxy-based Resin: A solder mask is applied over the PCB to insulate and protect copper traces from environmental factors. The material is typically an epoxy-based resin.
- Silkscreen:
- Legend Ink: The silkscreen layer includes component markings, labels, and other information. Legend ink is often epoxy-based and is applied to the PCB surface.
- Components:
- Semiconductors: Integrated circuits (ICs), microcontrollers, and other semiconductor devices are typically made of silicon or other semiconductor materials.
- Resistors and Capacitors: These components are often made of ceramic, tantalum, or electrolytic materials.
- Inductors and Transformers: Cores may be made of ferrite or other magnetic materials.
- Connectors and Switches: Various materials such as plastics, metals, and alloys are used for connectors and switches.
- Surface Finish:
- Gold, Tin, or Lead: Surface finishes are applied to exposed copper pads to prevent oxidation. Common surface finishes include gold plating, tin plating, or lead-free finishes.
- Adhesives and Encapsulation:
- Epoxy Resin: Adhesives are used for component attachment, and encapsulation materials protect sensitive components. Epoxy resins are commonly used for these purposes.
- Substrate Support:
- FR-4 or Other Insulating Material: Support structures or insulating layers may be made from the same substrate material used for the PCB or other insulating materials.
- Conformal Coating:
- Polymeric Materials: Conformal coatings are applied to protect PCBs from environmental factors. These coatings are often polymeric materials like acrylic, silicone, or urethane.
- Lead-free Alloys (if applicable):
- Tin, Silver, Copper (SnAgCu): Lead-free solder alloys, such as SnAgCu, have become more prevalent due to environmental considerations.
7. How does PGF address the growing demand for eco-friendly practices in custom PCBA manufacturing?
PGF is committed to sustainability. We incorporate eco-friendly materials and green manufacturing practices into our custom PCBA manufacturing process, aligning with global efforts to reduce environmental impact.
- Lead-Free Soldering:
- Use lead-free solder alloys (e.g., SnAgCu) to eliminate the use of hazardous lead-based solders. Lead-free soldering is not only environmentally friendly but also complies with regulations such as RoHS.
- Recycling of Materials:
- Establish a system for recycling materials used in the PCB assembly process. This can include recycling waste solder, copper, and other metals, as well as recycling or properly disposing of electronic waste.
- Energy Efficiency:
- Implement energy-efficient practices in the manufacturing process. This includes optimizing equipment usage, adopting energy-efficient machinery, and scheduling production during off-peak energy consumption periods.
- Reduced Chemical Usage:
- Minimize the use of hazardous chemicals in the PCB assembly process. Choose environmentally friendly cleaning agents and fluxes, and ensure proper disposal or recycling of chemicals to prevent environmental contamination.
- Water Conservation:
- Implement practices to conserve water usage in the manufacturing process. This may involve recycling water used in cleaning processes and adopting water-efficient technologies.
- Reusable Packaging:
- Use reusable packaging materials for transporting components and PCBs. Minimize the use of single-use packaging to reduce waste generation.
- RoHS Compliance:
- Ensure compliance with regulations such as the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS). RoHS restricts the use of certain hazardous materials, including lead, in electronic products.
- Design for Disassembly and Recycling:
- Design PCBs with disassembly and recycling in mind. Use modular designs that allow for easy component replacement and recycling at the end of the product’s life cycle.
- Employee Training:
- Provide training to employees on eco-friendly practices and the importance of environmental stewardship. Encourage a culture of environmental responsibility within the organization.
- Waste Reduction:
- Implement strategies to reduce waste generation during the manufacturing process. This includes optimizing production processes to minimize scrap and waste materials.
8. Can PGF create flexible and rigid-flex PCB designs for custom PCBA projects?
Absolutely. PGF’s expertise extends to crafting flexible and rigid-flex PCB designs, offering clients versatile solutions that can adapt to various form factors. This flexibility ensures that our custom PCBA projects can meet the evolving needs of modern electronics.
Conclusion: Partnering for Custom Excellence
Navigating the world of custom PCBA is made simpler with PGF Technology Group’s commitment to transparency, quality, and innovation. Whether you are a seasoned industry professional or new to the world of electronic manufacturing, our comprehensive guide aims to provide insights into the intricacies of custom electronic assemblies.
Ready to Explore Custom PCBA Solutions?
Contact PGF Technology Group today for custom electronic assemblies that epitomize precision, quality, and innovation. Let’s bring your unique electronic vision to life.